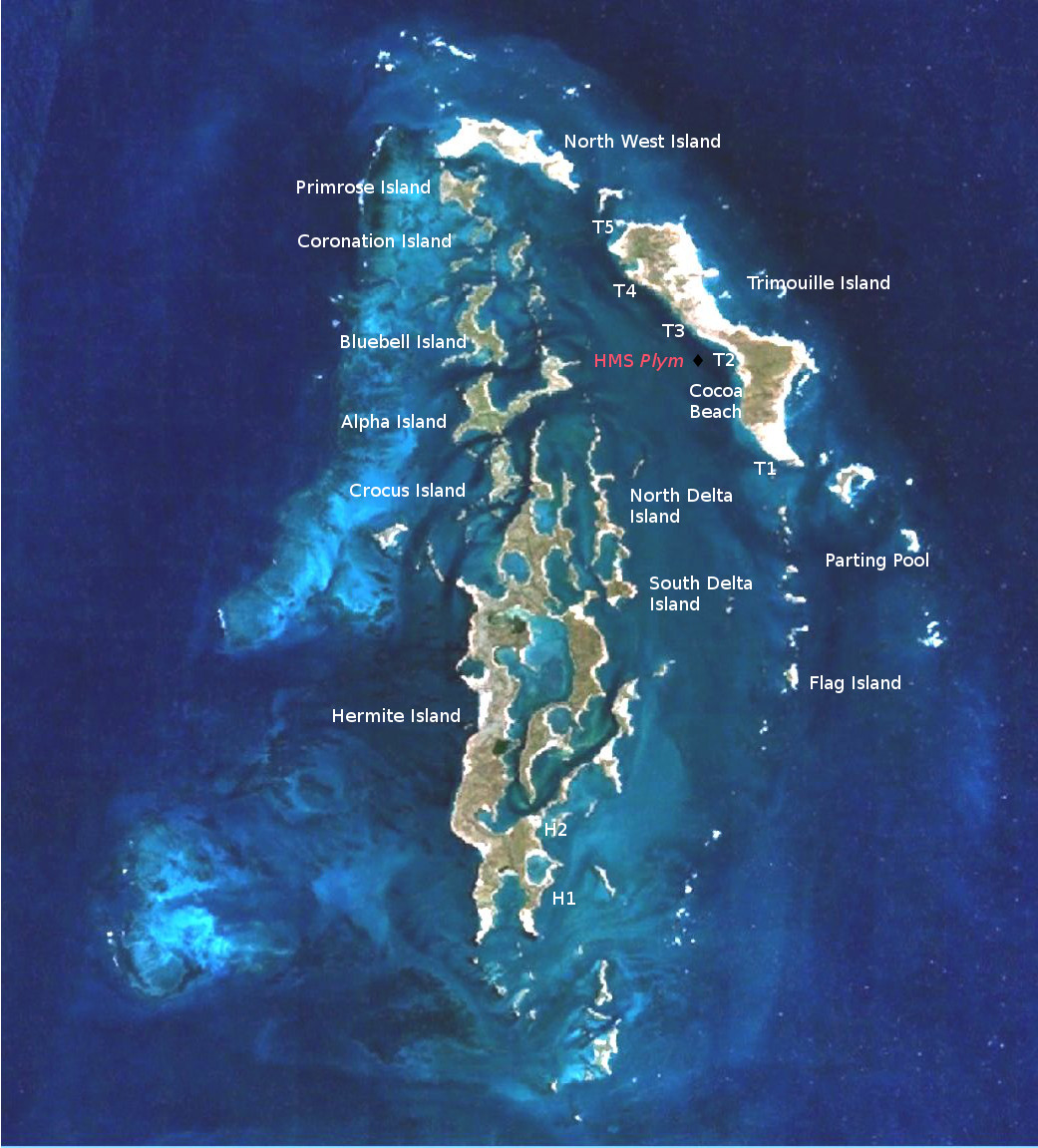
The Montebello Islands were the site of three atmospheric nuclear weapon tests by the British military: one in 1952, and two in 1956.
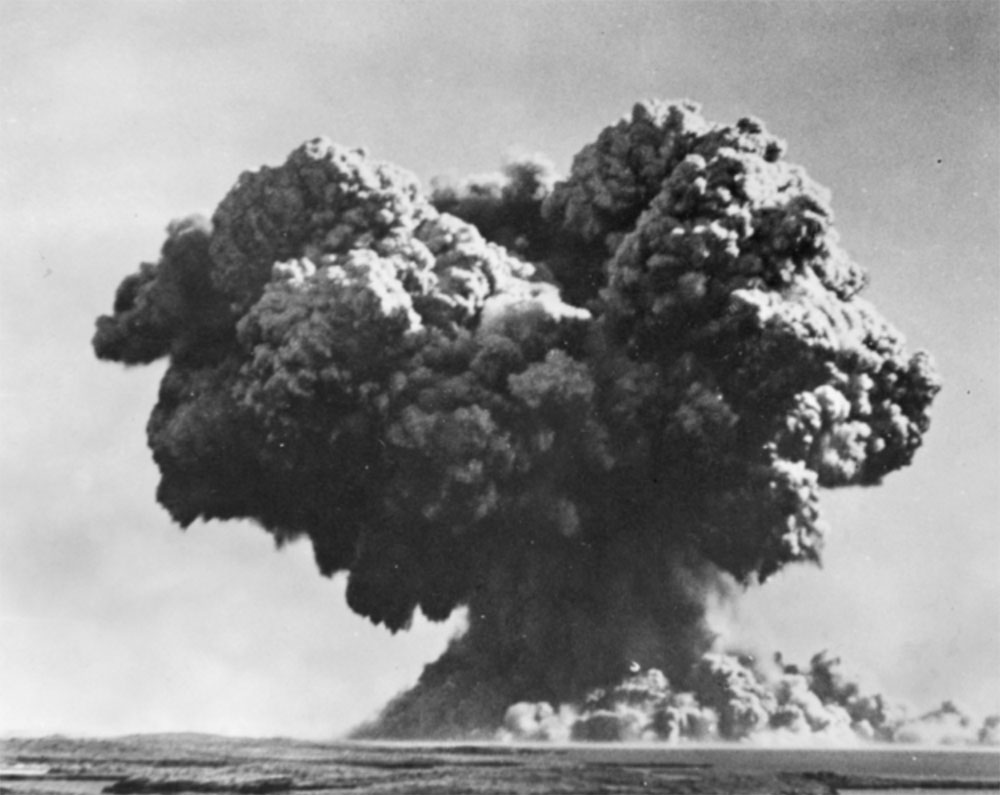
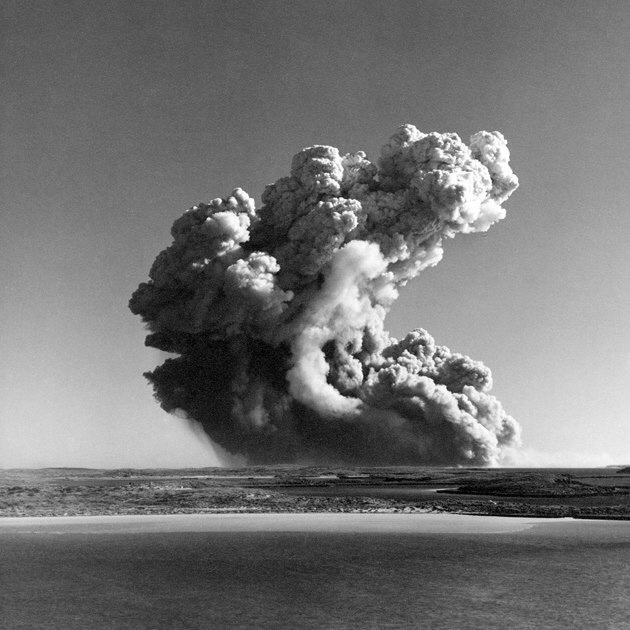
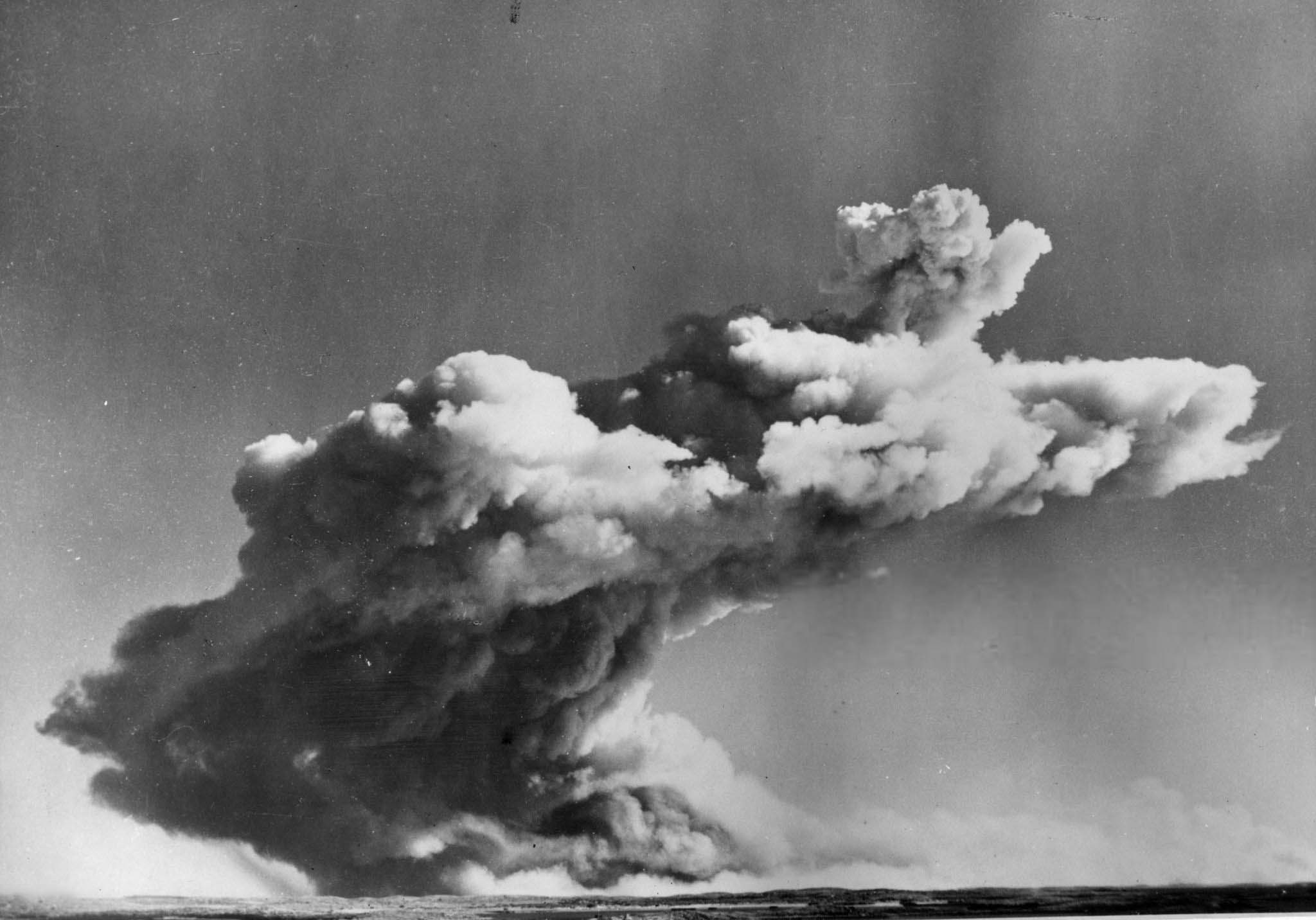
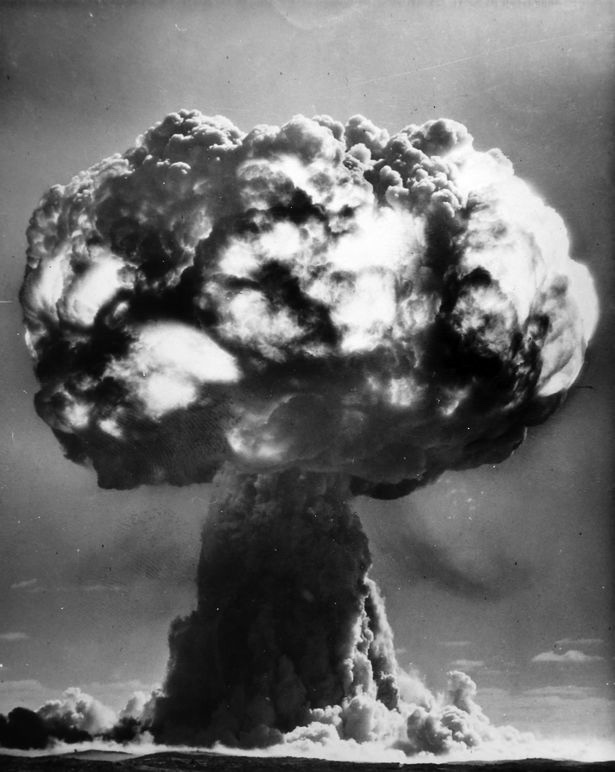
While subsequent British tests were conducted at sites on mainland Australia, in 1956 there were two land-sited tower-mounted tests, on Trimouille and Alpha Islands. The second of these, codenamed “Mosaic G2”, was the largest nuclear explosion in Australia, with an official yield of 60 kilotons. Mosaic G2 was later described as an “exceptionally dirty explosion”, whose fallout contaminated large areas of mainland Australia, as far away as the Queensland towns of Mount Isa, Julia Creek, Longreach and Rockhampton.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Operation_Hurricane
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Montebello_Islands
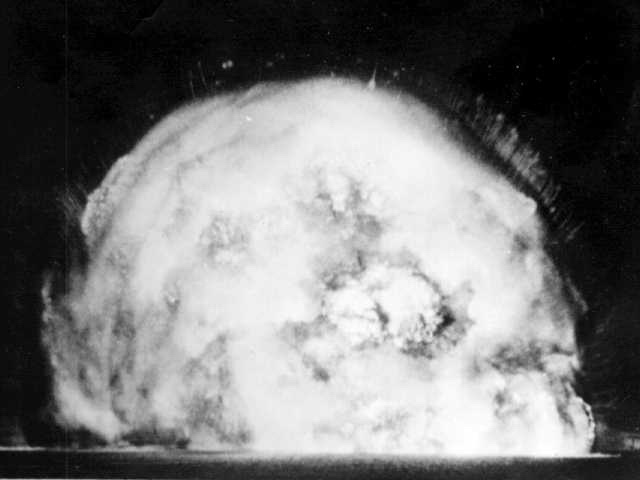
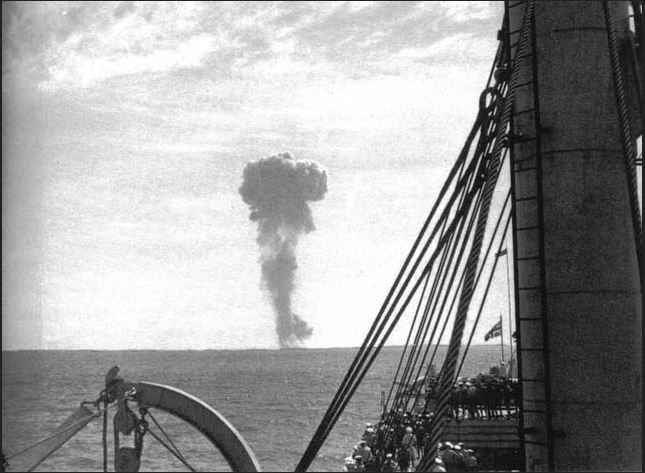
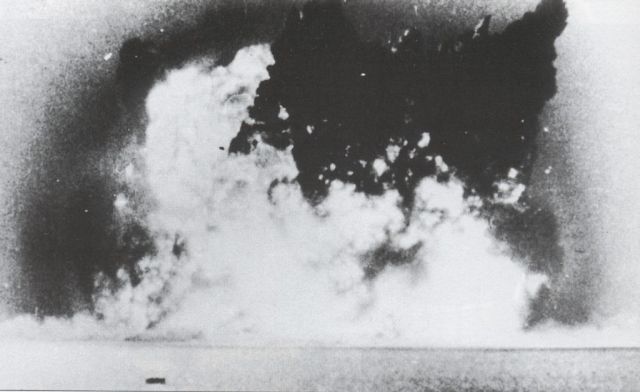
Operation Hurricane, 3 October 1952
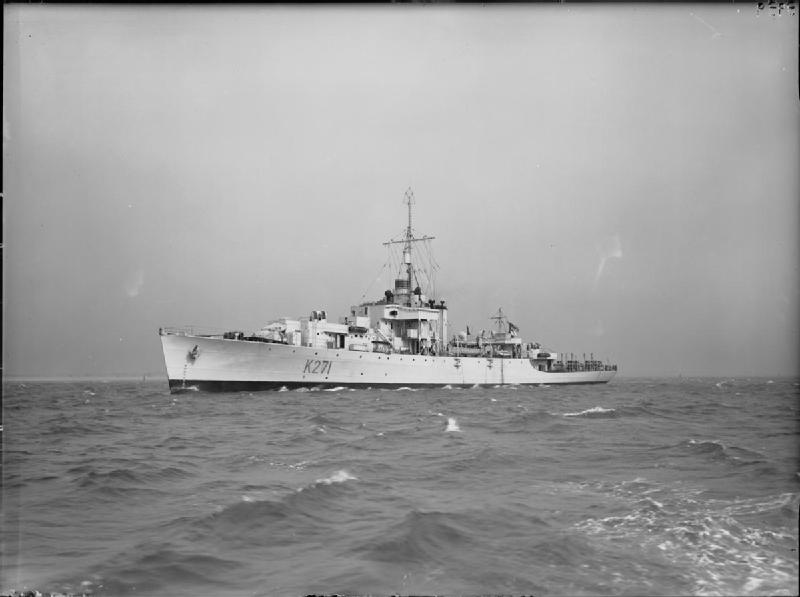
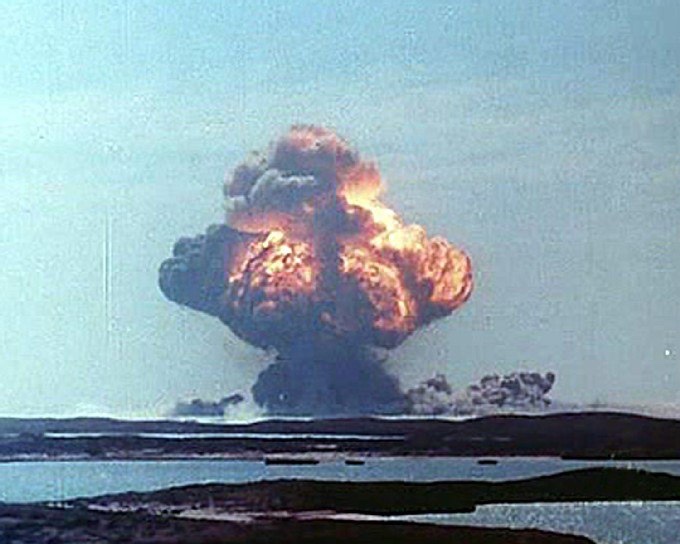
HMS Plym, moored in Main Bay on Trimouille Island, was the site of Operation Hurricane, the first-ever atomic weapon tested by the United Kingdom, on 3 October 1952. A plutonium implosion device was detonated in Main Bay, Trimouille Island, in the Montebello Islands in Western Australia. With the success of Operation Hurricane, Britain became the third nuclear power, after the United States and the Soviet Union.
Operation Mosaic G1 16 May 1956 and G2 19 June 1956
Operation Mosaic was a series of two British nuclear tests conducted in the Montebello Islands in Western Australia on 16 May and 19 June 1956. These tests followed the Operation Totem series and preceded the Operation Buffalo series. The second test in the series was the largest ever conducted in Australia.